Cloud computing has emerged as the cornerstone of modern business operations, propelling innovation, scalability, and operational efficiency to new heights. As organizations increasingly embrace cloud migration, the complexity of securing these environments multiplies, presenting a significant challenge. This is where Cloud Security Architecture steps in—a critical framework meticulously designed to fortify cloud-based systems, safeguarding data, and applications against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
This comprehensive blog delves into the intricacies of cloud security architecture, elucidating its foundational principles, pivotal components, inherent challenges, and industry best practices. This blog will provide you with a profound understanding of how to meticulously design and implement a robust architecture that aligns seamlessly with your organization’s unique needs.

The insights provided aim to empower you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the intricate world of cloud computing with confidence, ensuring your organization’s data and applications are safeguarded against potential risks. By extending your knowledge and implementing these strategies, you can future-proof your cloud infrastructure, maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving digital ecosystem.
What is Cloud Security Architecture?
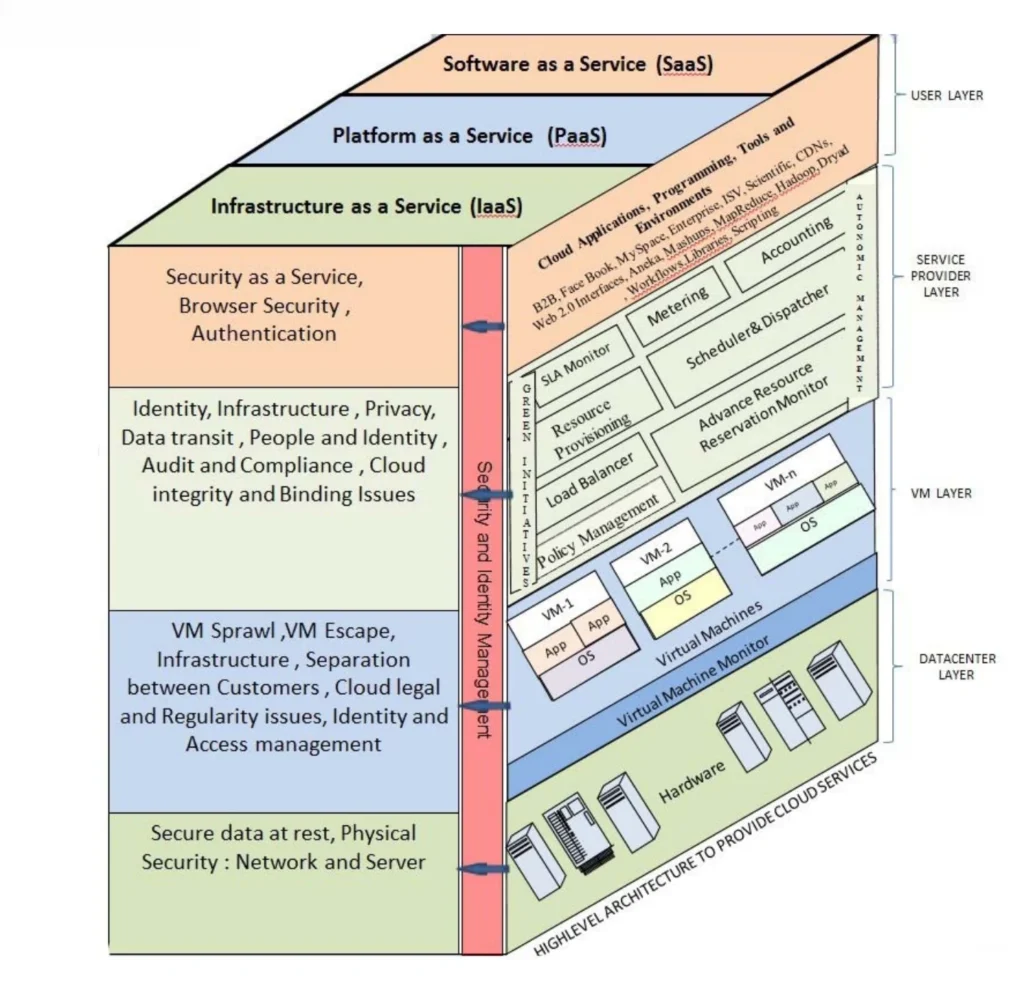
This Security Architecture refers to the structured design and implementation of security controls, policies, and technologies to protect cloud environments. It encompasses the strategies and frameworks used to secure data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in the cloud. Unlike traditional on-premises security, cloud security architecture must account for the shared responsibility model, where both the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer play a role in securing the environment.
The primary goal of this architecture is to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of data and services while mitigating risks such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and service disruptions.
Why is Cloud Security Architecture Important?
The shift to cloud computing has introduced new security challenges, including:-
- Shared Responsibility
While CSPs like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide robust infrastructure security, customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and access controls.
- Dynamic Environments
Cloud environments are highly dynamic, with resources being spun up and down in real-time. This makes it challenging to maintain consistent security controls.
- Increased Attack Surface
The cloud’s distributed nature expands the attack surface, making it easier for adversaries to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Requirements
Organizations must adhere to industry-specific regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, which require robust security measures.
A well-designed architecture addresses these challenges by providing a holistic framework for securing cloud environments.
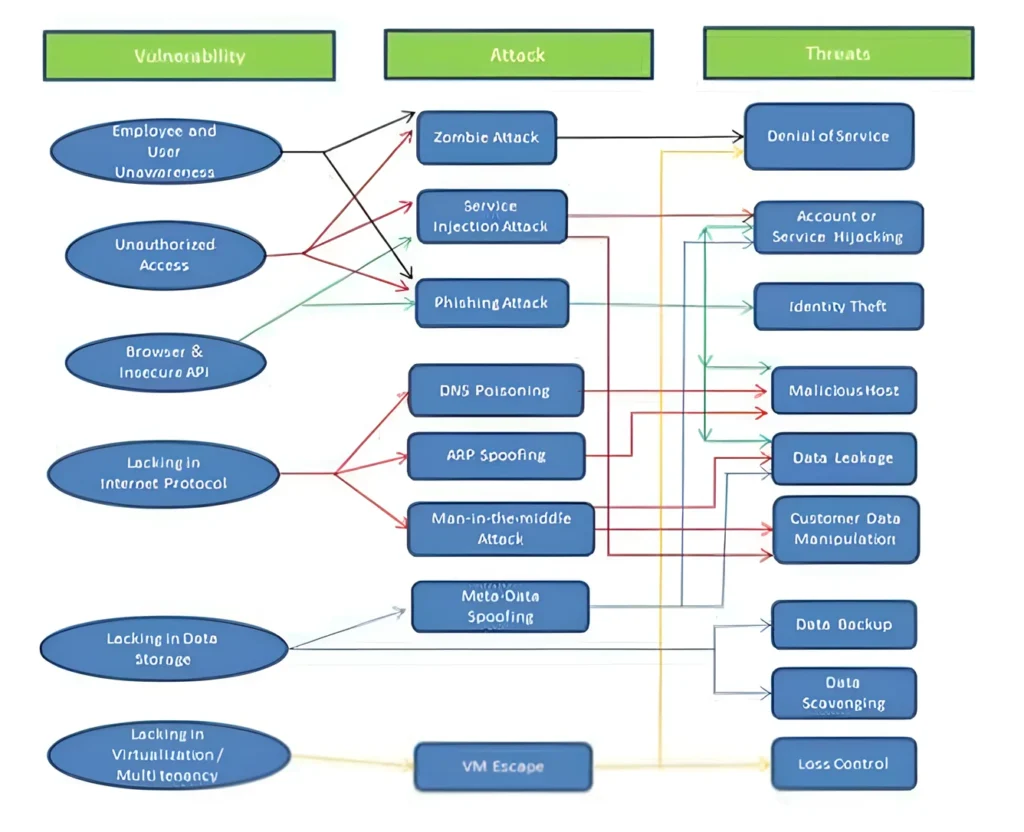
Key Components of Cloud Security Architecture
An architecture comprises several interconnected components, each playing a vital role in protecting the cloud ecosystem. Let’s explore these components in detail:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is the cornerstone of cloud security. It ensures that only authorized users and systems can access cloud resources.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Least privilege principles
- Regular access reviews
2. Data Encryption
Encryption is essential for protecting data at rest, in transit, and in use. The architecture should include:
- End-to-end encryption for data in transit (e.g., TLS/SSL)
- Encryption for data at rest (e.g., AES-256)
- Key management solutions to securely store and manage encryption keys
3. Network Security
Securing the network layer is critical to prevent unauthorized access and data exfiltration.
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) to isolate resources
- Firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Secure VPNs and Direct Connect for hybrid cloud environments
4. Threat Detection and Response
Proactively identifying and mitigating threats is essential for maintaining cloud security.
- Continuous monitoring of cloud environments
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems
- Automated incident response workflows
5. Compliance and Governance
Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements is a key aspect of cloud security.
- Regular audits and assessments
- Policy enforcement through tools like Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
- Data residency and sovereignty considerations
6. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
A resilient cloud security must include plans for disaster recovery and business continuity.
- Regular backups of critical data
- Redundant systems and failover mechanisms
- Testing and updating recovery plans
Challenges in Cloud Security Architecture
Designing and implementing a cloud security architecture is not without its challenges. Some of the most common hurdles include:
1. Complexity of Multi-Cloud Environments
Many organizations use multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize costs. However, managing security across disparate platforms can be complex and resource-intensive.
2. Lack of Visibility
The dynamic nature of cloud environments makes it difficult to maintain visibility into all resources and activities. This lack of visibility can lead to misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
3. Skill Gaps
Cloud security requires specialized knowledge and skills. Many organizations struggle to find and retain talent with expertise in cloud security architecture.
4. Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, requiring organizations to stay ahead of new attack vectors and techniques.
5. Compliance Complexity
Navigating the complex web of regulatory requirements can be challenging, especially for organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Check Out More at – CSPM Explained: Boost Cloud Security Posture Management
Best Practices for Building a Robust Cloud Security Architecture
To overcome these challenges and build a resilient cloud security architecture, consider the following best practices:
1. Adopt a Zero Trust Model
The Zero Trust model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It requires strict identity verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location.
2. Leverage Automation
Automation can help streamline security processes, such as patch management, threat detection, and incident response. Tools like CSPM and SIEM can automate monitoring and enforcement of security policies.
3. Implement Defense in Depth
A layered security approach, known as defense in depth, ensures that multiple security controls are in place to protect against various attack vectors. This includes firewalls, encryption, IAM, and intrusion detection systems.
4. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Regularly assess your cloud environment for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and audits can help identify and address security gaps.
5. Educate and Train Employees
Human error is a leading cause of security breaches. Provide regular training to employees on cloud security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and securing access credentials.
6. Collaborate with Your CSP
Work closely with your cloud service provider to understand their security offerings and how they align with your organization’s needs. Leverage built-in security features and tools provided by the CSP.
The Future of Cloud Security Architecture
As cloud adoption continues to grow, so too will the importance of the security architecture. Emerging trends and technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and quantum computing, will shape the future of cloud security. Organizations must stay agile and adapt their security strategies to address new threats and opportunities.
Must Check Out: Cloud Security Provider
Final Remarks
Cloud Security Architecture is not just a technical requirement—it’s a business imperative. In an era where data breaches and cyberattacks are on the rise, a robust security architecture is essential for protecting sensitive information, maintaining customer trust, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
By understanding the key components, challenges, and best practices of cloud security architecture, organizations can build a resilient foundation for their cloud environments. Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or looking to enhance your existing security posture, investing in a well-designed cloud security architecture is a step toward a safer, more secure future.
FAQs: Cloud Security Architecture
What is Cloud Security Architecture?
Cloud Security Architecture refers to the structured design and implementation of security controls, policies, and technologies to protect cloud environments. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of data and services while mitigating risks like data breaches and unauthorized access.
Why is Cloud Security Architecture important for businesses?
With the rise of cloud adoption, businesses face challenges like shared responsibility, dynamic environments, and increased attack surfaces. Cloud Security Architecture provides a holistic framework to address these challenges, ensuring compliance, reducing risks, and safeguarding sensitive data.
What are the key components of Cloud Security Architecture?
The key components include Identity and Access Management (IAM), data encryption, network security, threat detection and response, compliance and governance, and disaster recovery and business continuity. Each component plays a vital role in securing cloud environments.
What are the common challenges in implementing Cloud Security Architecture?
Challenges include managing multi-cloud environments, lack of visibility into resources, skill gaps in cloud security, evolving cyber threats, and navigating complex compliance requirements across different jurisdictions.